The earlier versions of vLLM Semantic Router relied on classification-based routing, a straightforward approach where user queries are classified into one of 14 MMLU domain categories, and then routed to corresponding models. While this worked for basic scenarios, we quickly discovered its limitations when building production AI systems for enterprises.
Consider this real-world scenario: A user asks, “I need urgent help reviewing a security vulnerability in my authentication code.” The classification-based router would identify this as a “computer science” query and route it to a general coding model. But it misses critical context:
- The urgency signal that requires immediate attention
- The security sensitivity that demands specialized expertise and jailbreak protection
- The code review intent that benefits from reasoning capabilities
- The authentication complexity that needs careful analysis
This single example reveals the fundamental constraint: classification-based routing captures only one dimension of user intent—the domain—while ignoring the rich, multi-dimensional signals embedded in natural language queries.
Today, we’re introducing the Signal-Decision Architecture—a complete reimagining of semantic routing that scales from 14 fixed categories to unlimited intelligent routing decisions. This new architecture combines multi-dimensional signal extraction, flexible decision logic with AND/OR operators, and built-in plugin orchestration to deliver production-ready semantic intelligence.
The Problem: Why Classification-Based Routing Doesn’t Scale
The previous vLLM Semantic Router architecture followed a simple pipeline:
User Prompt → MMLU Domain Classification → Model Selection
This approach has several fundamental limitations that prevent it from scaling to enterprise requirements.
Single-Dimensional Analysis
Classification-based routing only considers the domain or subject matter of the query. It cannot capture:
- Urgency signals: “urgent”, “immediate”, “critical”
- Security sensitivity: “vulnerability”, “exploit”, “breach”
- Intent types: code review, architecture design, troubleshooting
- Complexity levels: simple FAQ vs. complex reasoning tasks
- Compliance requirements: PII handling, regulatory constraints
Real Impact: A medical query about “urgent patient data breach” gets routed to a medical model but lacks PII protection and security filtering—potentially violating HIPAA compliance.
Fixed Category Constraint
Limited to 14 predefined MMLU categories (math, physics, computer science, business, etc.), making it impossible to:
- Create custom categories for specific business domains
- Define fine-grained routing rules within a domain
- Scale beyond academic subject classification
Real Impact: An enterprise with 50+ specialized use cases (legal contracts, financial compliance, medical diagnostics, code security audits) cannot express their routing requirements within 14 categories.
Inflexible Logic
Cannot combine multiple conditions or implement complex routing strategies:
- No support for AND/OR logic: “route to expert model only when query is both urgent AND security-related”
- No priority-based selection when multiple conditions match
- No conditional plugin application based on signal combinations
Real Impact: Cannot implement layered routing strategies like “high-priority security issues get reasoning + jailbreak protection, while general questions get cached responses.”
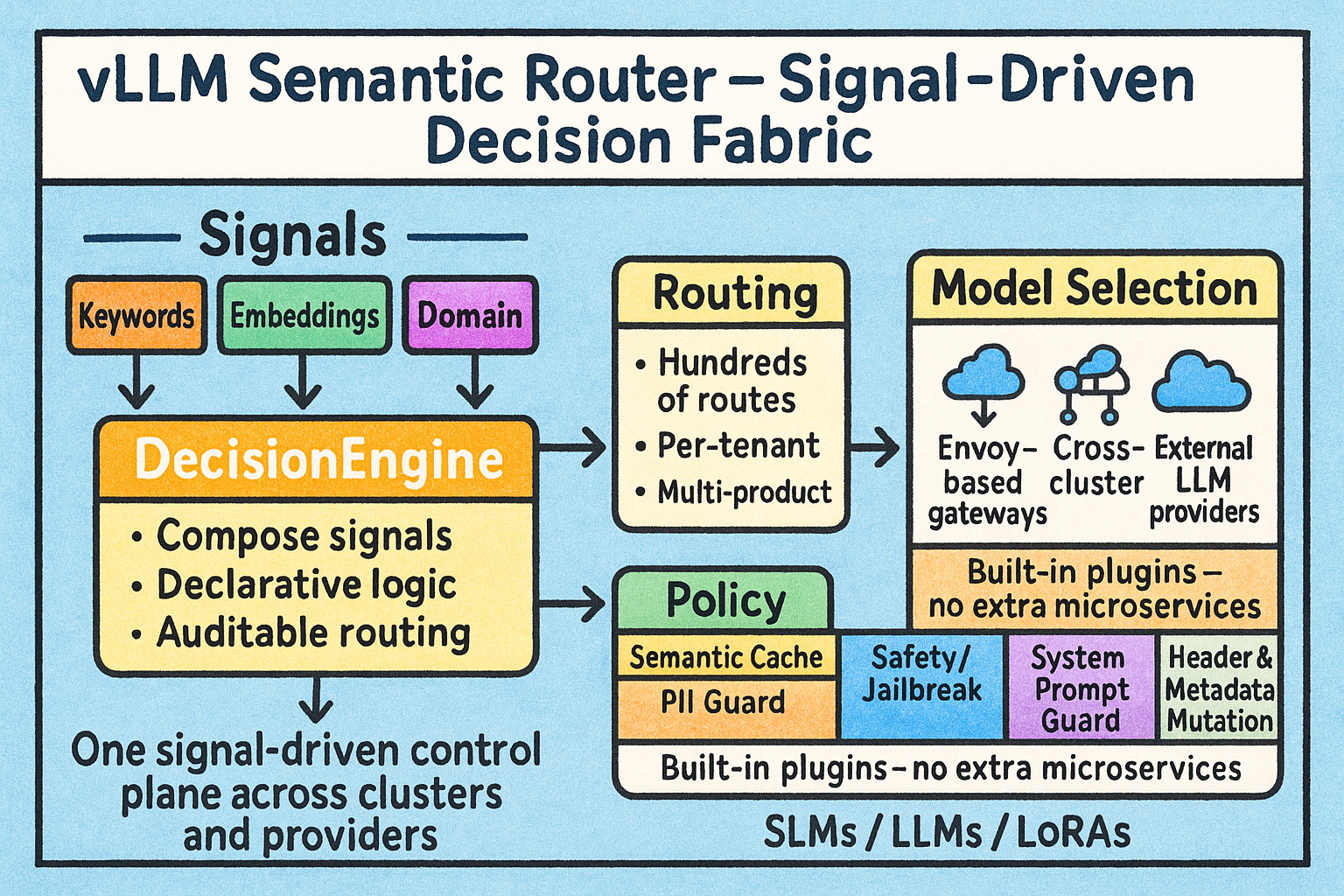
Introducing Signal-Decision Architecture
The Signal-Decision Architecture fundamentally reimagines semantic routing by separating signal extraction from routing decisions and introducing a flexible decision engine with built-in plugin orchestration.
Architecture Overview
The new architecture introduces three key innovations:
- Multi-Signal Extraction: Captures multiple dimensions of user intent simultaneously
- Decision Engine: Combines signals using flexible AND/OR logic with priority-based selection
- Plugin Chain: Provides built-in intelligence for caching, security, and optimization
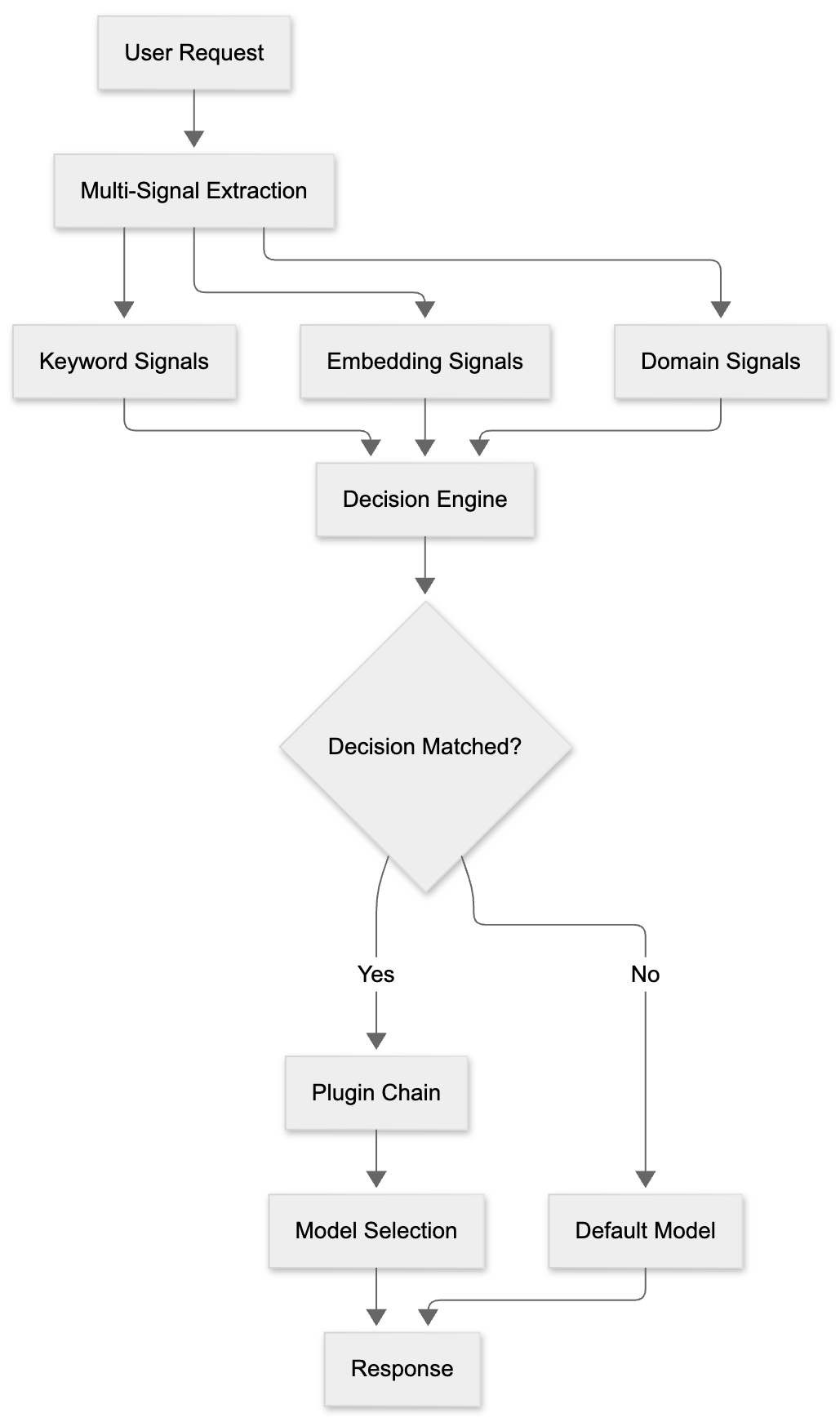
Complete Request Flow
Core Concepts
Signals: Multi-Dimensional Prompt Analysis
Instead of relying solely on domain classification, the Signal-Decision Architecture extracts three complementary types of signals from each user query. Each signal type leverages different AI/ML techniques and serves distinct purposes in the routing decision process.
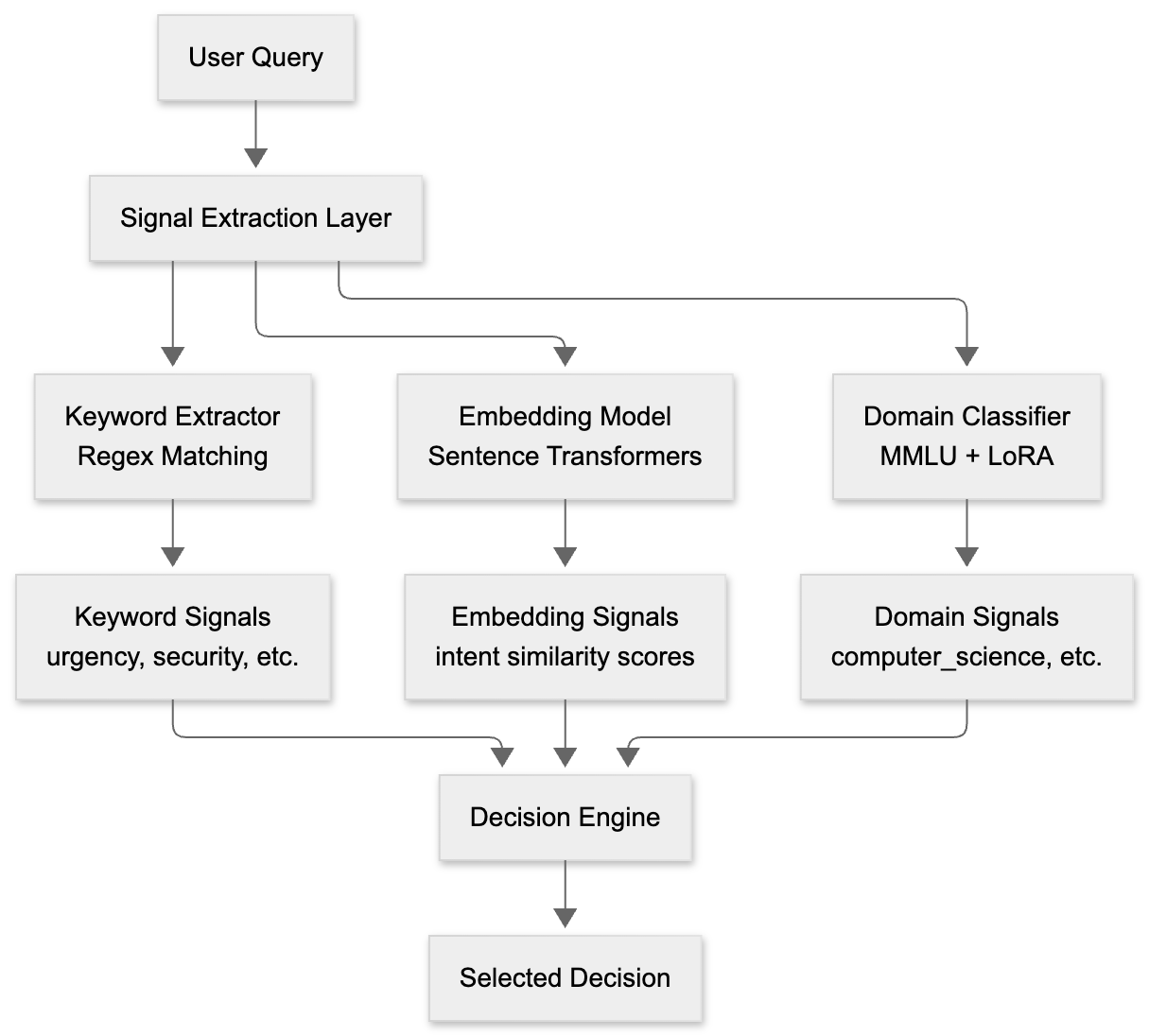
Keyword Signals: Interpretable Pattern Matching
Keyword signals use regex-based pattern matching to detect specific terms or phrases in user queries. This approach provides human-interpretable routing logic—you can easily understand why a query matched a particular rule by examining the keywords.
Technical Approach:
- Compiled regex patterns for efficient matching
- Support for AND/OR boolean operators
- Case-sensitive and case-insensitive modes
- No model inference required (zero ML overhead)
Key Advantage - Interpretability: Unlike black-box ML models, keyword signals provide complete transparency. When debugging routing decisions, you can trace exactly which keywords triggered which rules. This is critical for compliance auditing and troubleshooting production issues.
Use Cases:
- Detect urgency markers: “urgent”, “immediate”, “asap”, “critical”
- Identify security keywords: “vulnerability”, “exploit”, “breach”, “CVE”
- Flag compliance terms: “HIPAA”, “GDPR”, “PII”, “confidential”
- Recognize intent patterns: “code review”, “architecture design”, “troubleshooting”
Embedding Signals: Scalable Semantic Understanding
Embedding signals use neural embedding models to compute semantic similarity between user queries and candidate phrases. This approach provides scalable semantic matching that understands intent beyond exact keyword matches.
Technical Approach:
- Pre-computed embeddings for candidate phrases (offline)
- Runtime query embedding using lightweight models (e.g., sentence-transformers)
- Cosine similarity computation with configurable thresholds
- Multiple aggregation strategies: max (any match), mean (average similarity), any (threshold-based)
Key Advantage - Scalability: Embedding-based matching scales to thousands of candidate phrases efficiently. Adding new routing patterns doesn’t require retraining models—simply add new candidate phrases and compute their embeddings. This enables rapid iteration and customization for specific business domains.
Use Cases:
- Intent understanding: “I need help” → “technical support request”
- Paraphrase matching: “How do I fix this bug?” ≈ “debugging assistance”
- Cross-lingual routing: Semantic similarity works across languages with multilingual embeddings
- Fuzzy matching: Handles typos, abbreviations, and informal language
Domain Signals: Dataset-Driven Classification
Domain signals use MMLU-trained classification models to identify the academic or professional domain of user queries. This approach provides dataset-driven domain expertise with support for custom domain expansion.
Technical Approach:
- Fine-tuned classification models on MMLU dataset (14 base categories)
- Support for custom domain expansion via LoRA adapters
- Multi-label classification for queries spanning multiple domains
- Confidence scoring for domain predictions
Key Advantage - Extensibility via LoRA: While the base model covers 14 MMLU categories, enterprises can train lightweight LoRA adapters to add private domain categories without retraining the entire model. For example:
- Healthcare: Add “medical_imaging”, “clinical_trials”, “pharmaceutical_research”
- Finance: Add “risk_modeling”, “algorithmic_trading”, “regulatory_compliance”
- Legal: Add “contract_law”, “intellectual_property”, “litigation_support”
This enables organizations to extend domain classification to their specific verticals while maintaining the base model’s general knowledge.
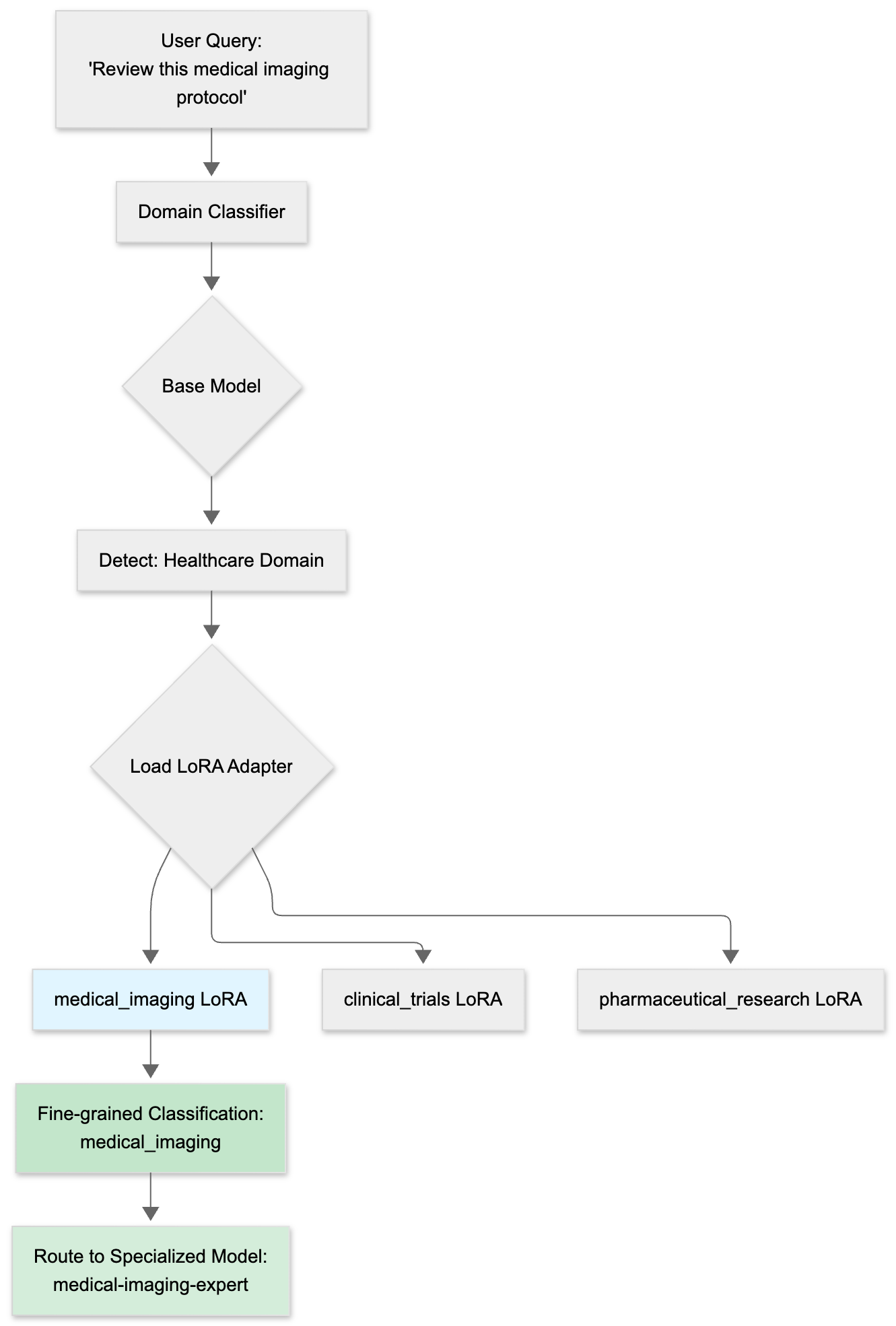
Use Cases:
- Route to domain-specific expert models (math queries → math-expert)
- Apply domain-appropriate policies (medical queries → PII protection)
- Select specialized knowledge bases (legal queries → legal document retrieval)
- Trigger domain-specific plugins (code queries → syntax validation)
Signal Comparison
| Signal Type | Technique | Interpretability | Scalability | Extensibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Keyword | Regex matching | High (transparent rules) | Medium (manual patterns) | Manual addition |
| Embedding | Neural embeddings | Low (black-box similarity) | High (thousands of phrases) | Add phrases dynamically |
| Domain | MMLU + LoRA | Medium (domain labels) | Medium (14+ categories) | LoRA adapters for custom domains |
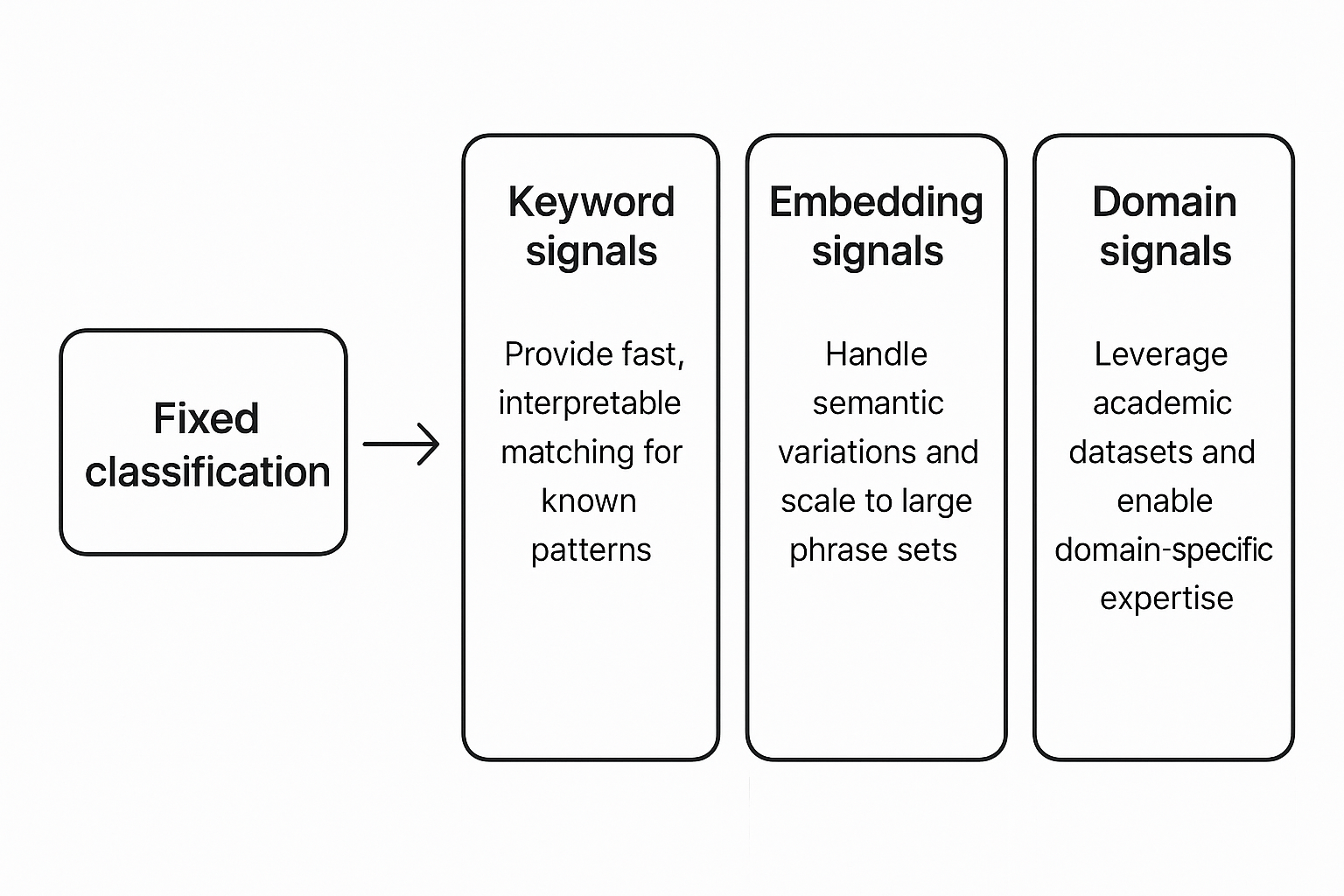
Why Three Signal Types?
The three signal types are complementary, not redundant:
- Keyword signals provide fast, interpretable matching for known patterns
- Embedding signals handle semantic variations and scale to large phrase sets
- Domain signals leverage academic datasets and enable domain-specific expertise
By combining all three, the Signal-Decision Architecture captures multiple dimensions of user intent simultaneously, enabling far more sophisticated routing logic than any single signal type could achieve.
Decisions: Flexible Routing Logic
Decisions are the core routing rules that combine multiple signals using AND/OR logic to determine model selection and plugin configuration.
Decision Structure
Each decision consists of:
Signal Combination: AND/OR logic combining multiple signal conditions
- AND: All conditions must match (high precision)
- OR: Any condition matches (high recall)
Priority: Integer value for conflict resolution when multiple decisions match
- Higher priority wins
- Enables layered routing strategies
Model Reference: Specifies which model (and optional LoRA adapter) to use
- Supports base models with domain-specific LoRA adapters
- Configures reasoning mode and effort level
Plugin Chain: Ordered list of plugins to apply
- Semantic caching for cost optimization
- Jailbreak detection for security
- PII protection for compliance
- System prompt injection for behavior control
- Header mutation for metadata propagation
Decision Evaluation Flow
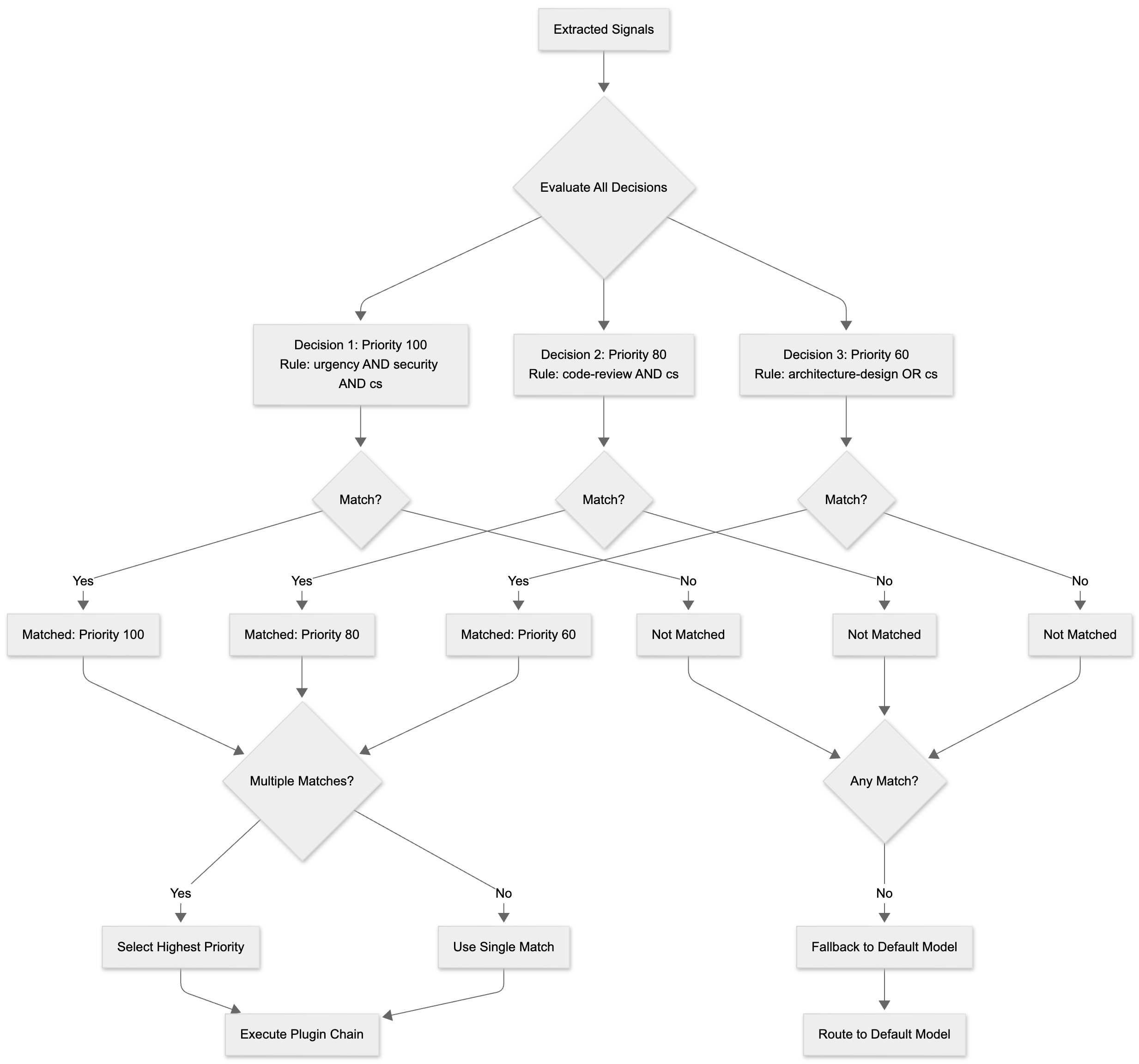
When multiple decisions match, the system selects the one with the highest priority. If no decisions match, the system falls back to the default model.
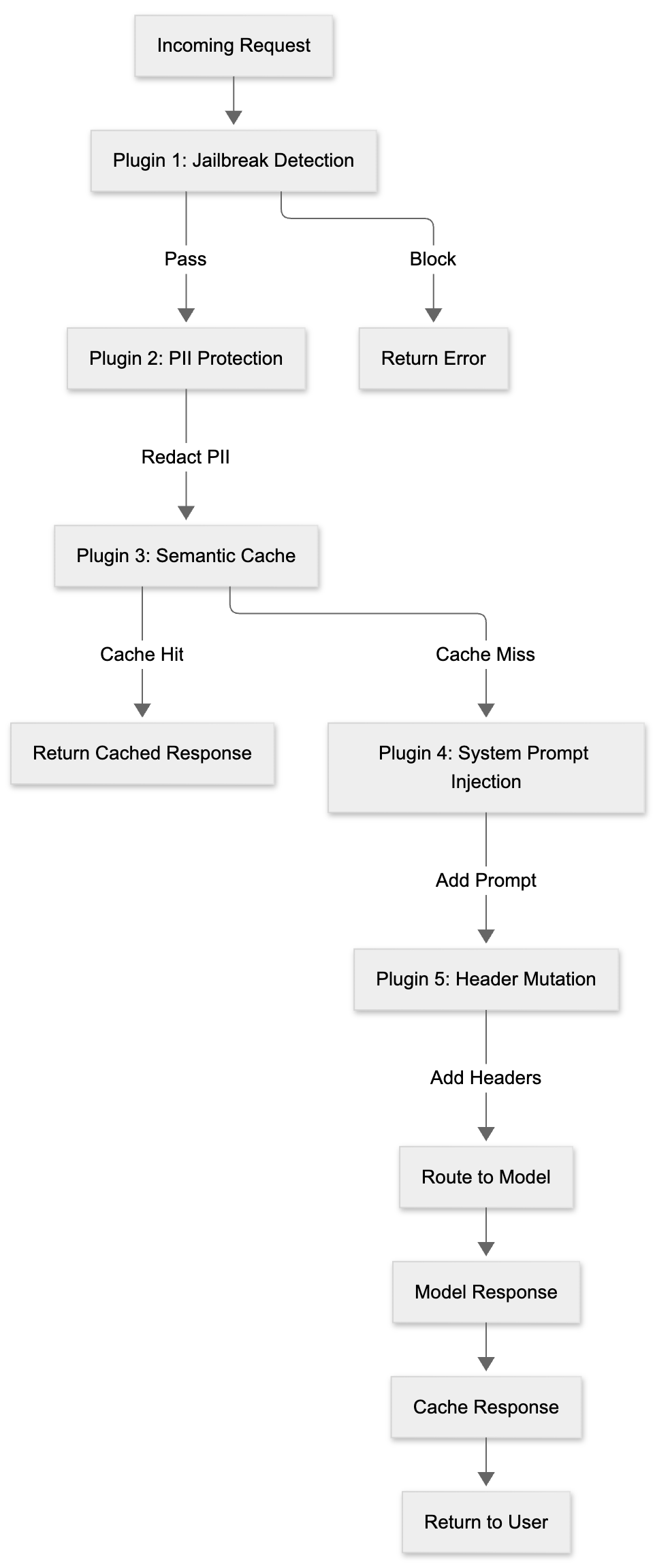
Plugins: Built-in Intelligence
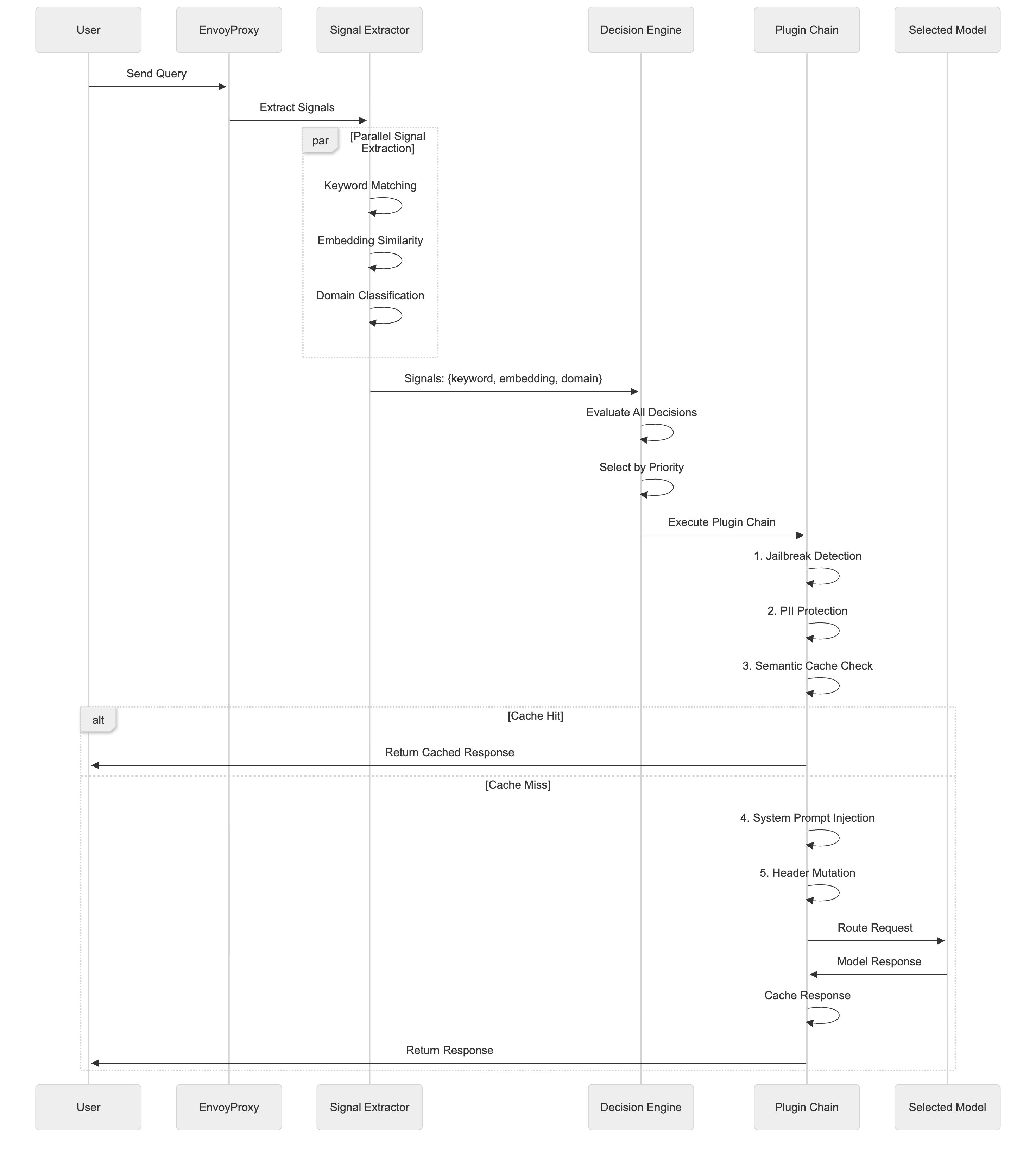
The architecture includes five built-in plugins that can be configured per decision:
| Plugin | Purpose | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| semantic-cache | Cache similar queries | Configurable similarity threshold, cost optimization |
| jailbreak | Detect prompt injection attacks | Threshold-based detection, request blocking |
| pii | Protect sensitive information | Redact/hash/mask modes, GDPR/HIPAA compliance |
| system_prompt | Inject custom instructions | Replace or insert mode, role customization |
| header_mutation | Modify HTTP headers | Add/update/delete headers, metadata propagation |
Plugins execute in the configured order, with each plugin able to modify the request, block execution, or add metadata for downstream processing.
Plugin Chain Execution Flow
Scaling from 14 to Unlimited
The Signal-Decision Architecture removes the fundamental constraint of fixed categories. Here’s how it scales:
Traditional Approach (Limited)
14 MMLU Categories → 14 Routing Rules → 14 Model Selections
Constraints:
- Cannot create custom categories
- Cannot combine multiple conditions
- Cannot apply different policies per rule
- Cannot scale beyond domain classification
Signal-Decision Approach (Unlimited)
3 Signal Types × N Conditions × AND/OR Logic → Unlimited Decisions
Capabilities:
- Create unlimited custom routing rules
- Combine multiple signals with flexible logic
- Apply unique plugin chains per decision
- Scale to enterprise complexity
Scalability Example
Consider an enterprise IT support system:
Traditional Routing: Limited to 14 domain-based routes
- “computer_science” → code-model
- “engineering” → engineering-model
- (12 more fixed categories)
Signal-Decision Routing: Hundreds of specialized routes
- Urgent + Security + Computer Science → security-expert + reasoning + jailbreak
- Code Review + High Complexity → architecture-model + reasoning
- FAQ + General → cached-model + semantic-cache
- Medical + PII Detected → medical-expert + PII-protection + disclaimer
- Legal + Confidential → law-expert + PII-hash + audit-headers
- (Hundreds more custom combinations)
Each decision can have unique model selection, reasoning configuration, and plugin chains—enabling fine-grained control at scale.
Kubernetes-Native Design
The Signal-Decision Architecture is designed for cloud-native environments with two Custom Resource Definitions (CRDs):
Complete Example: Enterprise IT Support System
Let’s walk through a complete example that demonstrates how IntelligentPool and IntelligentRoute work together to build an enterprise IT support routing system.
IntelligentPool: Define Model Pool
First, we define the available models and their LoRA adapters:
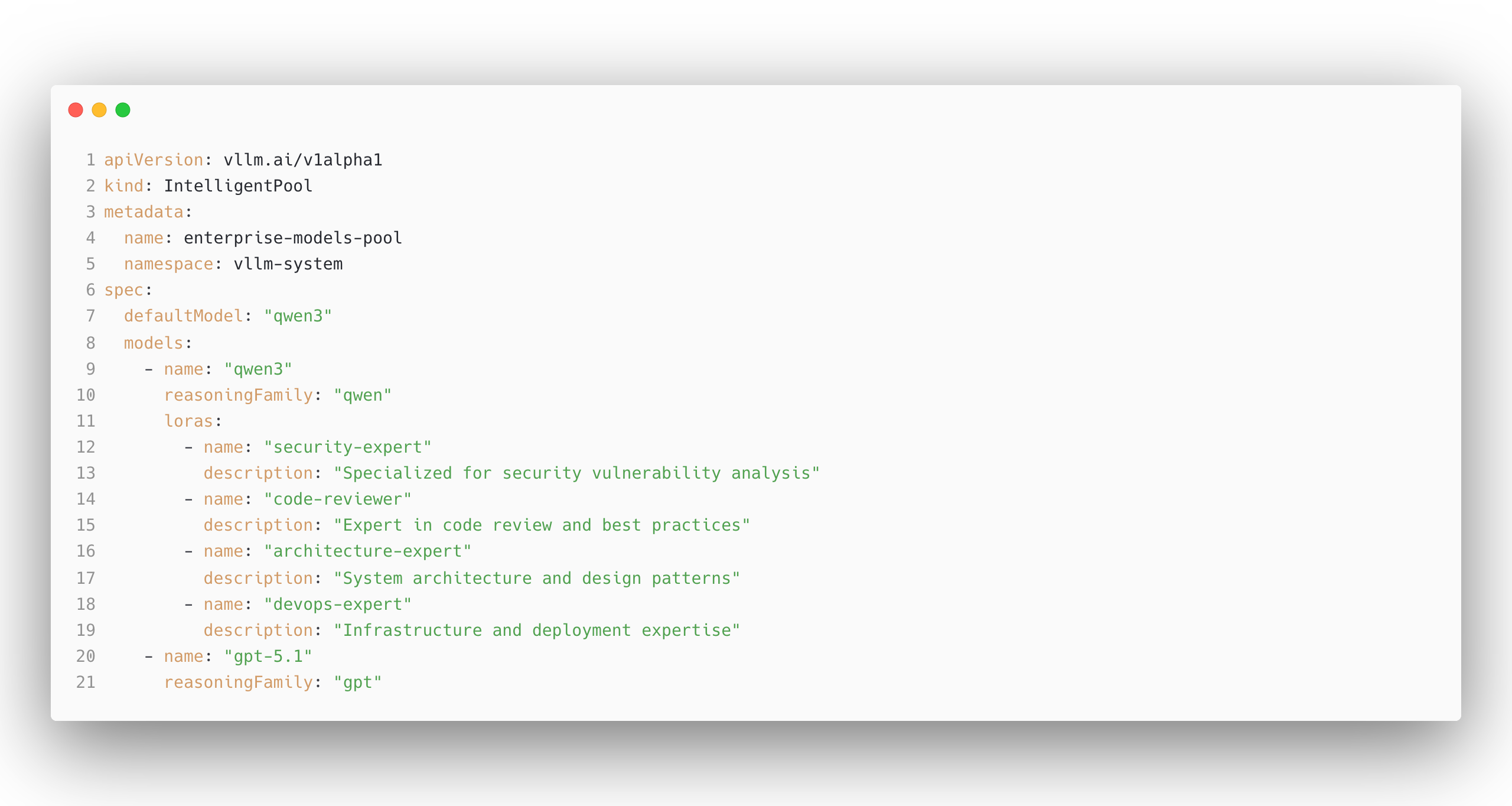
This pool defines:
- A base model “qwen3” with 4 specialized LoRA adapters
- A fallback “qwen3” model for non-specialized queries
- Reasoning family configuration for each model
IntelligentRoute: Define Routing Logic
Next, we define the routing decisions with multi-signal extraction:
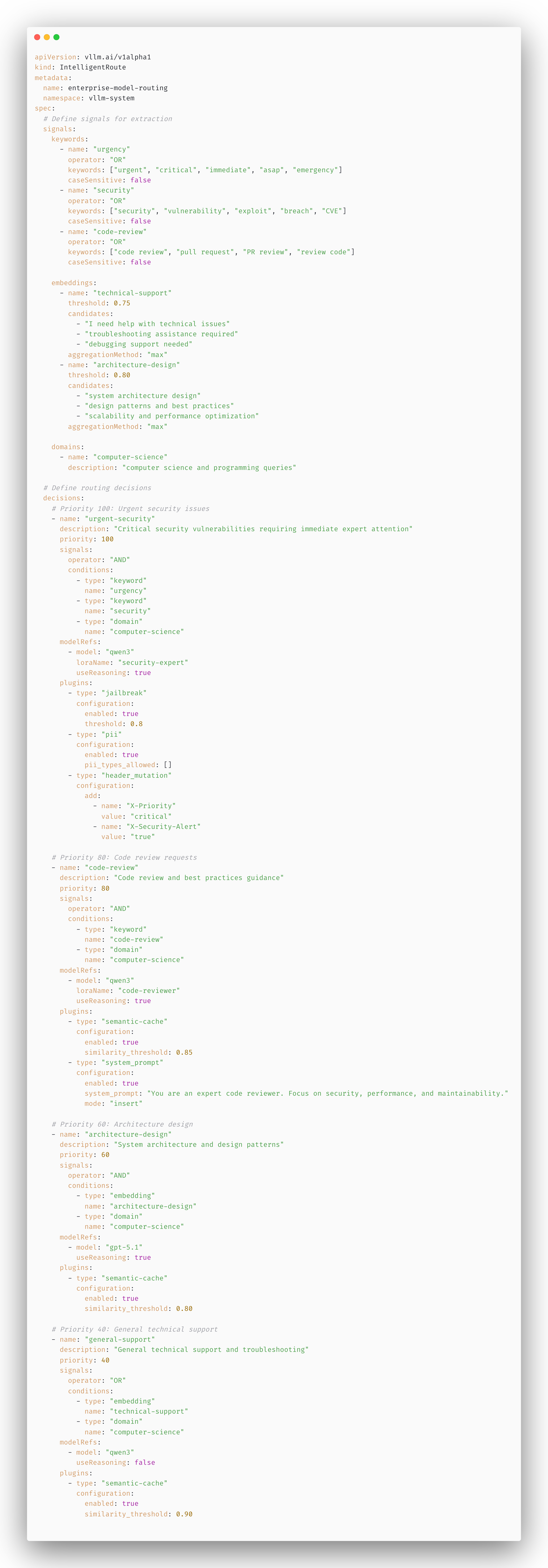
This configuration demonstrates:
Multi-Signal Extraction:
- 3 keyword signals (urgency, security, code-review)
- 2 embedding signals (technical-support, architecture-design)
- 1 domain signal (computer-science)
Layered Decision Logic:
- Priority 100: Urgent + Security + CS → security-expert + high reasoning + jailbreak + PII protection
- Priority 80: Code Review + CS → code-reviewer + medium reasoning + cache + custom prompt
- Priority 60: Architecture Design + CS → architecture-expert + high reasoning + cache
- Priority 40: General Support → base model + aggressive cache
Plugin Orchestration:
- Security-critical queries get jailbreak detection and PII protection
- Code reviews get semantic caching and custom system prompts
- Architecture queries get longer cache TTL (2h vs 1h)
- General queries get aggressive caching (0.90 threshold, 4h TTL)
Fallback Behavior:
- If no decision matches, route to defaultModel (“general-assistant”)
- If multiple decisions match, select highest priority
Dynamic Configuration Flow
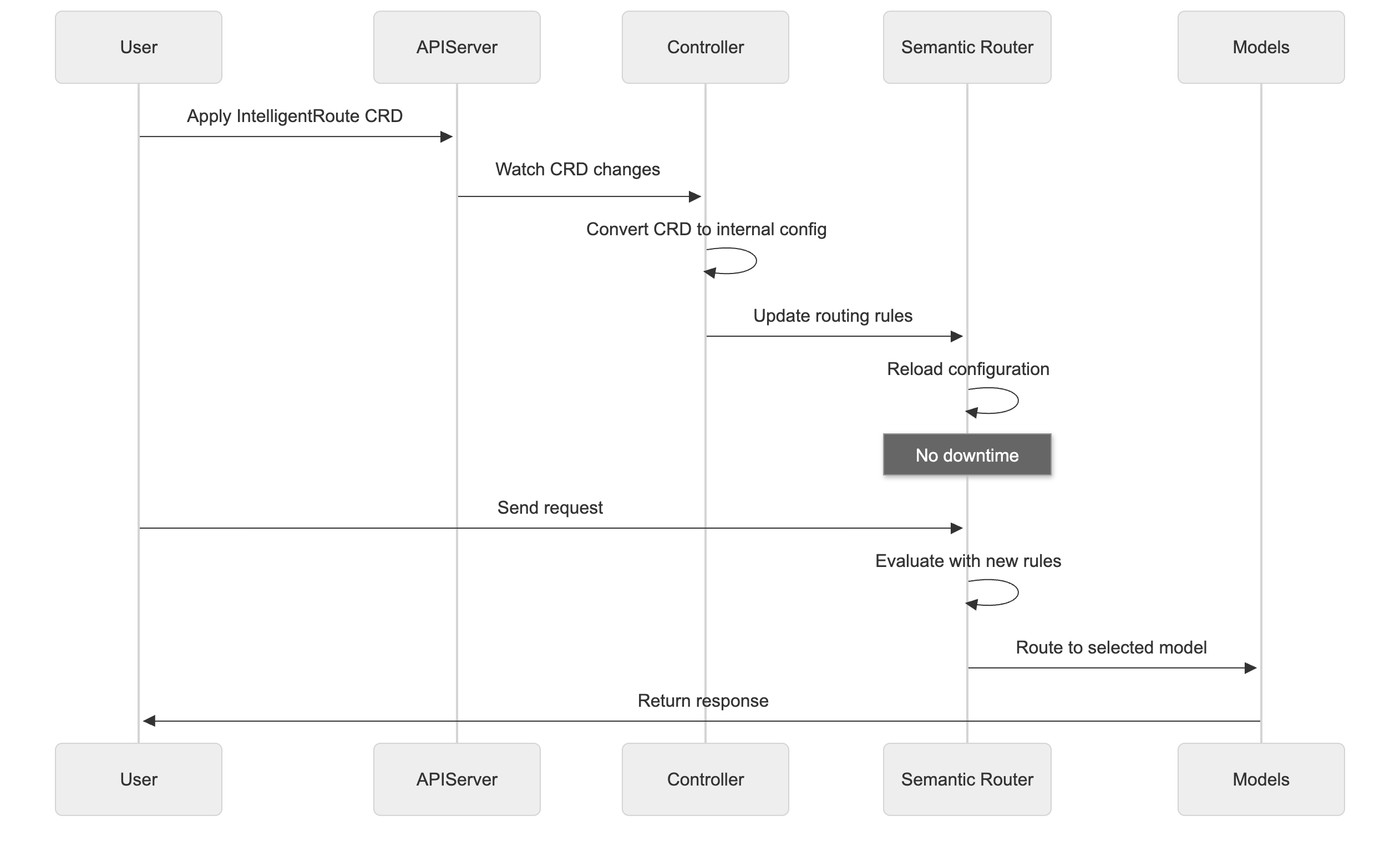
The Kubernetes-native design enables:
- Zero-downtime configuration updates
- GitOps workflows for change management
- Multi-cluster deployment strategies
- Namespace-based isolation and RBAC
Real-World Applications
Enterprise IT Support
Challenge: Route support tickets based on urgency, technical domain, and security sensitivity.
Solution: Multi-layered decisions with priority-based selection
- Priority 100: Urgent + Security + CS → security-expert + reasoning + jailbreak
- Priority 80: Technical Support + Debugging → code-expert + semantic-cache
- Priority 60: General Questions → general-model + aggressive-cache
Results: Appropriate model selection, cost optimization through caching, security protection for sensitive issues.
Healthcare Platform
Challenge: HIPAA compliance requiring PII protection and medical disclaimers.
Solution: Domain-based routing with mandatory compliance plugins
- Health Domain → medical-expert + PII-redaction + disclaimer-prompt + audit-headers
Results: Automatic PII protection, consistent disclaimers, audit trail for compliance.
Financial Services
Challenge: Multi-layered security with PII protection, jailbreak detection, and cost optimization.
Solution: Comprehensive plugin chain for financial queries
- Economics Domain → finance-expert + jailbreak + PII-hash + disclaimer + cache + compliance-headers
Results: Enterprise-grade security, regulatory compliance, cost efficiency.
Educational Platform
Challenge: Personalized learning experiences based on subject and learning intent.
Solution: Intent-based routing with customized teaching styles
- Math + Learning Intent → math-expert + reasoning + patient-tutor-prompt + cache
- Science + Tutorial → science-expert + engaging-educator-prompt
Results: Personalized teaching approaches, appropriate reasoning for complex topics, cost optimization.
Code Assistant
Challenge: Different complexity levels require different model capabilities.
Solution: Complexity-aware routing with reasoning control
- Architecture Design → reasoning-model + high-effort + complexity-header
- Code Review → code-expert + medium-reasoning + cache
- Simple Questions → code-expert + cache-only
Results: Optimal model selection, cost-effective reasoning usage, fast responses for simple queries.
Future Roadmap
The Signal-Decision Architecture provides a foundation for future enhancements across multiple dimensions:
Routing Core Performance Optimization
Radix Tree for Keyword Matching: Replace regex-based keyword matching with radix tree data structures to achieve faster pattern matching for thousands of keyword patterns. This will enable enterprises to define 10,000+ keyword rules with consistent performance.
HNSW Index for Embedding Search: Implement Hierarchical Navigable Small World (HNSW) graphs for approximate nearest neighbor search in embedding space. This will significantly improve embedding signal performance while supporting millions of candidate phrases.
Parallel LoRA for Decode-Only Models: Enable parallel execution of multiple LoRA adapters during the decode phase, allowing a single base model to serve multiple specialized domains simultaneously. This will reduce model switching overhead and improve throughput for multi-tenant deployments.
Feature Enhancements
Visual Configuration Console: Web-based UI for creating and managing decisions without YAML editing, with real-time validation and testing capabilities.
Custom Plugin Framework: SDK for developing custom plugins with community marketplace, enabling enterprises to build domain-specific intelligence layers.
Advanced Analytics: Real-time monitoring of decision performance, signal effectiveness, and cost optimization opportunities with ML-driven recommendations.
Model Evaluation via Multi-Turn Dialogue: Intelligent model selection through multi-turn conversation evaluation. The system automatically engages multiple candidate models in parallel conversations, using LLM-as-a-Judge to assess response quality across dimensions like coherence, relevance, safety, and domain expertise. This enables dynamic routing optimization based on actual model performance rather than static rules.
Intent-Aware Internal/External Model Selection: Smart routing between internal private models and external APIs (OpenAI, Anthropic, etc.) based on intent analysis. Sensitive data and proprietary information automatically route to internal models for privacy and compliance, while general queries leverage external APIs for broader knowledge. Cost, latency, and compliance requirements are balanced dynamically based on query characteristics.
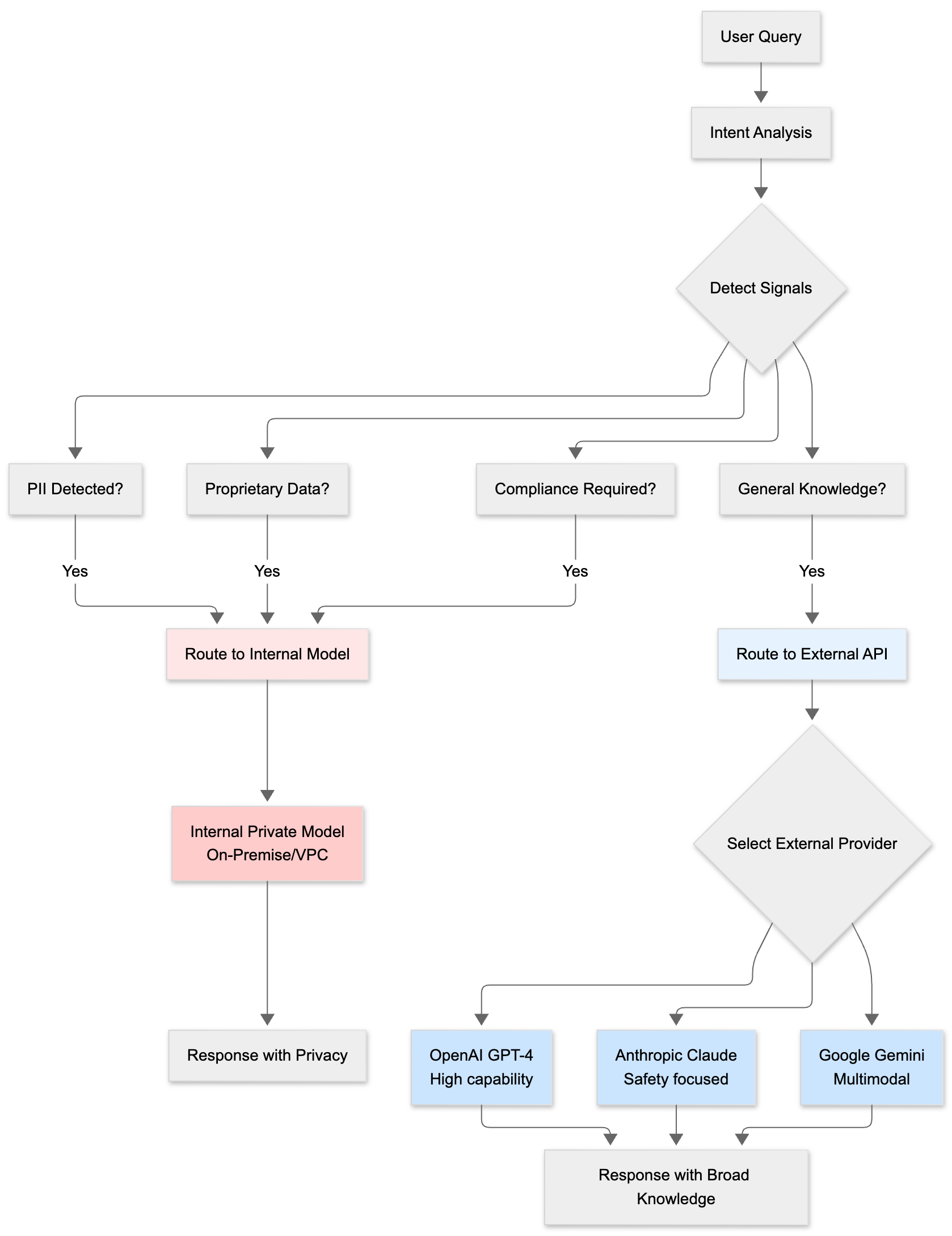
Conclusion
The Signal-Decision Architecture represents a fundamental shift in how we think about semantic routing. By moving from fixed classification to flexible signal-based decisions, we enable:
Unlimited Scalability: From 14 categories to unlimited custom routing rules
Multi-Dimensional Intelligence: Capture keyword, embedding, and domain signals simultaneously
Flexible Logic: Combine signals with AND/OR operators and priority-based selection
Built-in Security: Integrated plugins for jailbreak detection, PII protection, and compliance
Cloud-Native Design: Kubernetes CRDs with dynamic configuration and zero-downtime updates
Whether you’re building an enterprise AI gateway, a multi-tenant SaaS platform, or an industry-specific AI assistant, the Signal-Decision Architecture provides the scalability, flexibility, and intelligence needed for production deployments.
Getting Started
Ready to try Signal-Decision routing?
Join our community to share feedback and learn from other users building intelligent routing systems at scale.